Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence (1) Na+ diffuses into the cell and cause a local potential (2) Neurotransmitter binds with receptor on postsynaptic cell (3) Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) Membrane permeability to Na+ on postsynaptic cell increases (5) Action potential causes release of neu
Lecture 16- Synaptic transmission Flashcards | Memorang
Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence. (1) Sodium ions diffuse into the cell and cause a local potential (2) Neurotransmitter binds with receptor on post-synaptic cell (3) Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) Plasma membrane permeability to sodium ions increases (5) Action potential causes release of
Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
Arrange the events that occur during synaptic transmission (listed below) in the correct sequence: An action potential is propagated along a presynaptic neuron Neurotransmitter binds with receptors on the postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic neuron

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
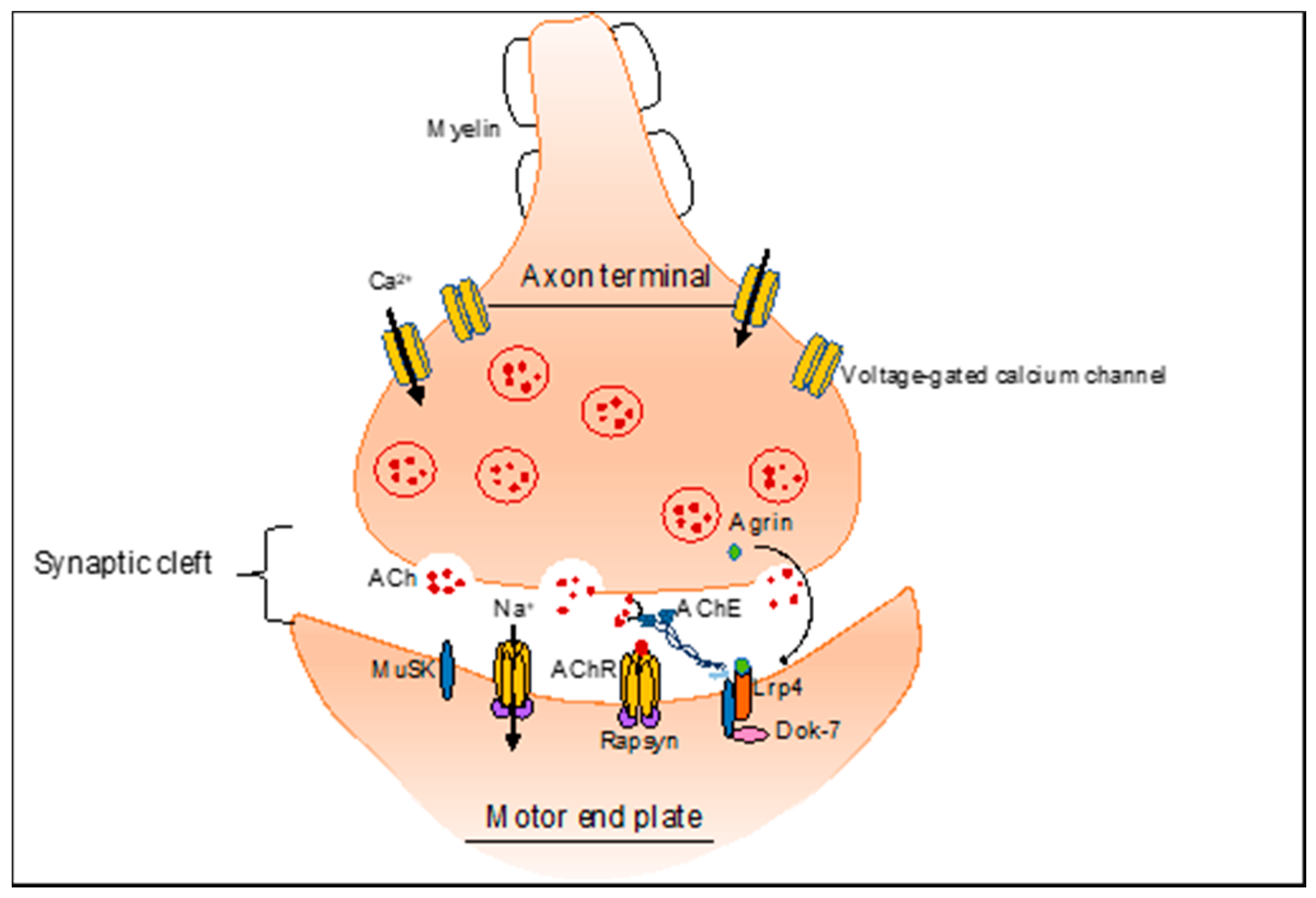
Solved In class we have discussed the sequence of events | Chegg.com What are the events in synaptic transmission? The presynaptic action potential reaches the synaptic knob. 2) The terminal is depolarised. 3) Voltage gated calcium channels in the presynaptic knob open. 4) Calcium enters through the calcium channels. 5) This calcium ions cause the fusion of synaptic vesicles to the presynaptic membrane.
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Arrange The Events Of Synaptic Transmission In Correct Sequence
What are the events in synaptic transmission? The presynaptic action potential reaches the synaptic knob. 2) The terminal is depolarised. 3) Voltage gated calcium channels in the presynaptic knob open. 4) Calcium enters through the calcium channels. 5) This calcium ions cause the fusion of synaptic vesicles to the presynaptic membrane. Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence. (1) Sodium ions diffuse into the cell and may trigger an action potential (2) Neurotransmitter binds to receptor on the postsynaptic cell membrane (3) Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) Membrane permeability to sodium ions on the postsynaptic cell increases
Cells | Free Full-Text | RNA Targeting in Inherited Neuromuscular Disorders: Novel Therapeutic Strategies to Counteract Mis-Splicing
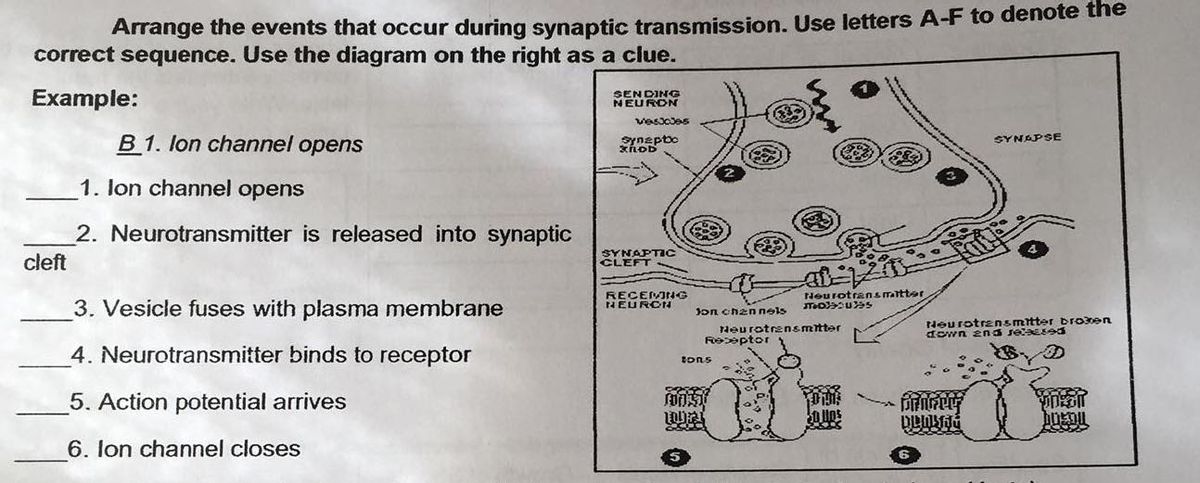
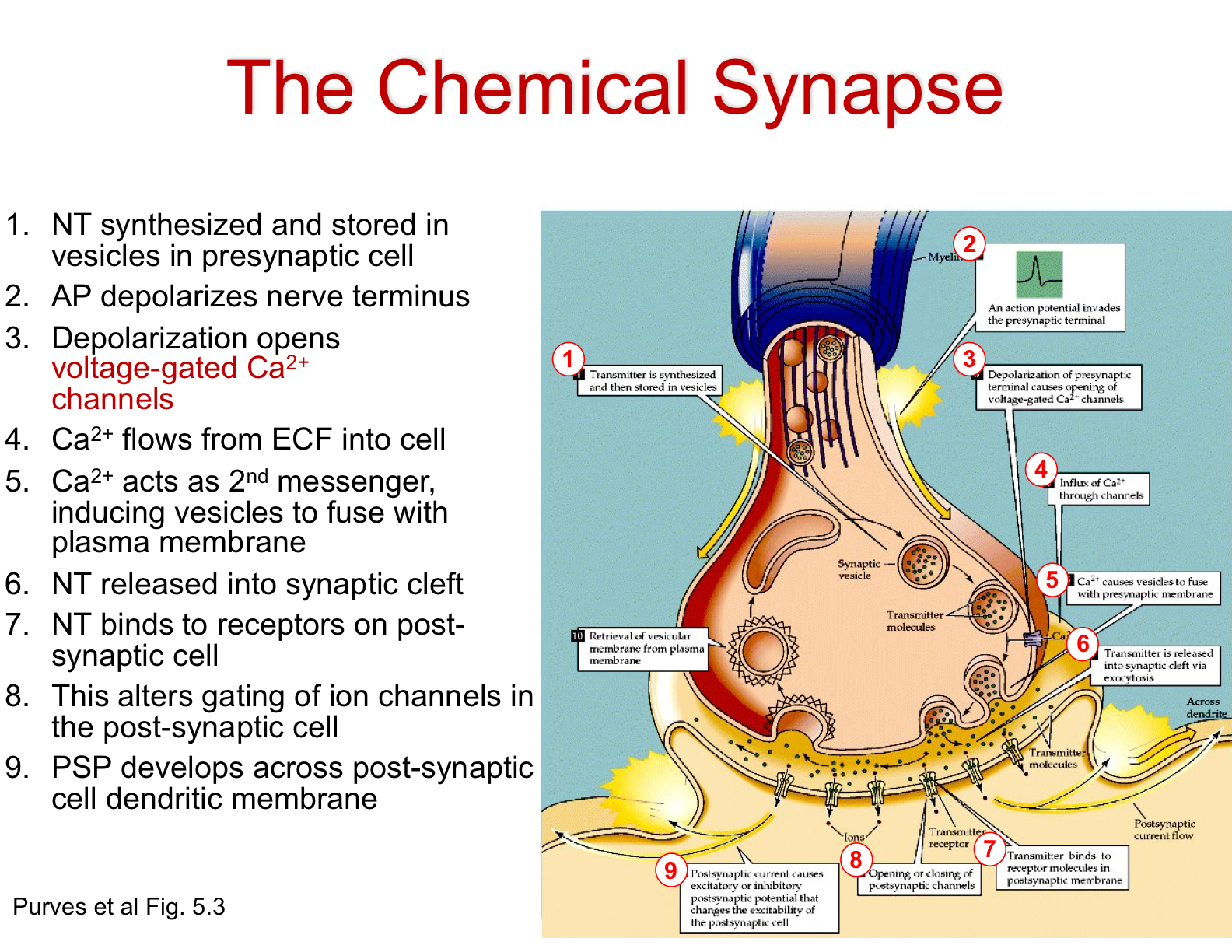
At a synapse, one neuron sends a message to a target neuron—another cell. Most synapses are chemical; these synapses communicate using chemical messengers. Other synapses are electrical; in these synapses, ions flow directly between cells. At a chemical synapse, an action potential triggers the presynaptic neuron to release neurotransmitters. SOLVED: Arrange the events that occur during synaptic transmission. Use letters A-F to denote the correct sequence. Use the diagram on the right as a clue: Example: Aewev; B1. Ion channel opens

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Answered: Arrange the events that occur during… | bartleby At a synapse, one neuron sends a message to a target neuron—another cell. Most synapses are chemical; these synapses communicate using chemical messengers. Other synapses are electrical; in these synapses, ions flow directly between cells. At a chemical synapse, an action potential triggers the presynaptic neuron to release neurotransmitters.

Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
Lecture 16- Synaptic transmission Flashcards | Memorang Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence (1) Na+ diffuses into the cell and cause a local potential (2) Neurotransmitter binds with receptor on postsynaptic cell (3) Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) Membrane permeability to Na+ on postsynaptic cell increases (5) Action potential causes release of neu
Source Image: memorang.com
Download Image
Solved In class we have discussed the sequence of events | Chegg.com Arrange the events that occur during synaptic transmission (listed below) in the correct sequence: An action potential is propagated along a presynaptic neuron Neurotransmitter binds with receptors on the postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft Neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic neuron

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Calendar – HGS Mathcomp Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence. (1) Sodium ions diffuse into the cell and cause a local potential (2) Neurotransmitter binds with receptor on post-synaptic cell (3) Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) Plasma membrane permeability to sodium ions increases

Source Image: mathcomp.uni-heidelberg.de
Download Image
Figure 3.16 Different Types of Synaptic Connections – ppt download What are the events in synaptic transmission? The presynaptic action potential reaches the synaptic knob. 2) The terminal is depolarised. 3) Voltage gated calcium channels in the presynaptic knob open. 4) Calcium enters through the calcium channels. 5) This calcium ions cause the fusion of synaptic vesicles to the presynaptic membrane.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Describe the sequence of events at a synapse, starting with an Action Potential in the presynaptic membrane and ending with the generation of an action potential in the Postsynaptic neuron. Also mention Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence. (1) Sodium ions diffuse into the cell and may trigger an action potential (2) Neurotransmitter binds to receptor on the postsynaptic cell membrane (3) Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) Membrane permeability to sodium ions on the postsynaptic cell increases

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
Answered: Arrange the events that occur during… | bartleby
Describe the sequence of events at a synapse, starting with an Action Potential in the presynaptic membrane and ending with the generation of an action potential in the Postsynaptic neuron. Also mention Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence. (1) Sodium ions diffuse into the cell and cause a local potential (2) Neurotransmitter binds with receptor on post-synaptic cell (3) Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) Plasma membrane permeability to sodium ions increases (5) Action potential causes release of
Solved In class we have discussed the sequence of events | Chegg.com Figure 3.16 Different Types of Synaptic Connections – ppt download Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence. (1) Sodium ions diffuse into the cell and cause a local potential (2) Neurotransmitter binds with receptor on post-synaptic cell (3) Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) Plasma membrane permeability to sodium ions increases