Jul 28, 2023The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. \(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
Paired T-test in Power BI using DAX – Ben’s Blog
This statistics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into hypothesis testing. It provides examples and practice problems that explains how to state

Source Image: projectpro.io
Download Image
Oct 5, 2022The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test: Null hypothesis (H0): There’s no effect in the population. Alternative hypothesis (HA): There’s an effect in the population. The effect is usually the effect of the independent variable on the dependent

Source Image: analyticssteps.com
Download Image
Inferential Statistics: Definition, Types + Examples | QuestionPro The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0: The null hypothesis: It is a statement about the population that either is believed to be true or is used to put forth an argument unless it can be shown to be incorrect beyond a reasonable doubt.

Source Image: blog.uxtweak.com
Download Image
A Statistical Test Involves The Following Null And Alternative Hypotheses
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0: The null hypothesis: It is a statement about the population that either is believed to be true or is used to put forth an argument unless it can be shown to be incorrect beyond a reasonable doubt. Apr 23, 2022An hypothesis test is a statistical decision; the conclusion will either be to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative, or to fail to reject the null hypothesis. The decision that we make must, of course, be based on the observed value x x of the data vector X X.
Preference Test vs. A/B Testing: which one should you choose? | UXtweak
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0, the —null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0. Test Statistics: Definition, Formulas & Examples | Outlier
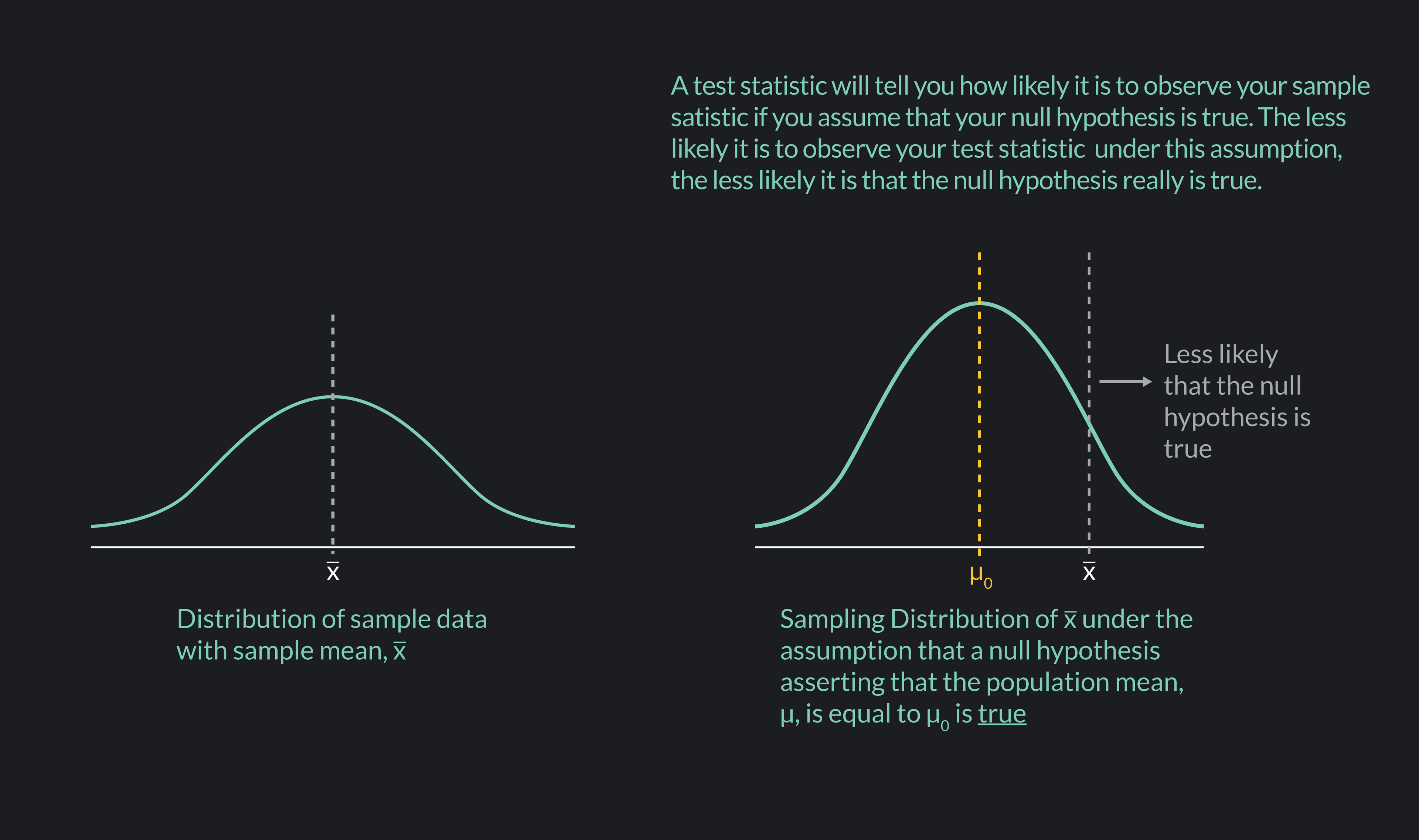
Source Image: articles.outlier.org
Download Image
Hypothesis Testing Examples | CFA Level 1 – AnalystPrep The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0, the —null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.

Source Image: analystprep.com
Download Image
Paired T-test in Power BI using DAX – Ben’s Blog Jul 28, 2023The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. \(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.

Source Image: datakuity.com
Download Image
Inferential Statistics: Definition, Types + Examples | QuestionPro Oct 5, 2022The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test: Null hypothesis (H0): There’s no effect in the population. Alternative hypothesis (HA): There’s an effect in the population. The effect is usually the effect of the independent variable on the dependent
Source Image: questionpro.com
Download Image
An Intuitive Guide To Various Statistical Tests | by Saksham Gulati | Medium State the null and alternative hypotheses. These two hypotheses need to be mutually exclusive, so if one is true then the other must be false. 2. Determine a significance level to use for the hypothesis. Decide on a significance level. Common choices are .01, .05, and .1. 3. Find the test statistic.

Source Image: sakshamgulati123.medium.com
Download Image
Hypothesis Testing: The Complete Beginner’s Guide | by Akash Dugam | Medium The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0: The null hypothesis: It is a statement about the population that either is believed to be true or is used to put forth an argument unless it can be shown to be incorrect beyond a reasonable doubt.

Source Image: dugamakash.medium.com
Download Image
SOLVED: A statistical test involves the following null and alternative hypotheses: H0: μ = 64, Ha: μ > 64. Which of the following describes a Type II error? A) Failing to reject Apr 23, 2022An hypothesis test is a statistical decision; the conclusion will either be to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative, or to fail to reject the null hypothesis. The decision that we make must, of course, be based on the observed value x x of the data vector X X.
 Download Image
Download ImageHypothesis Testing Examples | CFA Level 1 – AnalystPrep
SOLVED: A statistical test involves the following null and alternative hypotheses: H0: μ = 64, Ha: μ > 64. Which of the following describes a Type II error? A) Failing to reject This statistics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into hypothesis testing. It provides examples and practice problems that explains how to state
Inferential Statistics: Definition, Types + Examples | QuestionPro Hypothesis Testing: The Complete Beginner’s Guide | by Akash Dugam | Medium State the null and alternative hypotheses. These two hypotheses need to be mutually exclusive, so if one is true then the other must be false. 2. Determine a significance level to use for the hypothesis. Decide on a significance level. Common choices are .01, .05, and .1. 3. Find the test statistic.